Direct and Indirect Speech

Definition of Indirect Speech
Indirect speech is also known as reported speech, indirect narration, or indirect discourse. In grammar, when you report someone else’s statement in your own words without any change in the meaning of the statement, it is called indirect speech. Quoting a person’s words without using his own word and bringing about any change in the meaning of the statement is a reported speech. Look at the following sentences:
Direct Speech: She says, “I am a little bit nervous.”
Indirect Speech: She says that she is a little bit nervous.
In the first sentence, the reporter conveys the message of the girl using her actual words (e.g., “I am a little bit nervous.”) In the second sentence, the reporter conveys her message but in his own words without any change in the meaning. Thus, both direct and indirect speeches are two different ways of reporting a statement of person. In simple words, quoting a person using your own words is called an indirect speech.
Key Terminology
During the process, you will come across many important terms that you need to know better so that you can convert any direct speech into indirect speech easily and without any hassle. Consider the following sentences:
- Direct Speech: She says, “I am a little bit nervous.”
- Indirect Speech: She says that she is a little bit nervous.
Now consider the different grammatical aspects of both.
- Reporting Speech: The first part in the direct speech is called reporting speech.
- Reported Speech: The second part of the sentence, which is closed in inverted commas or quotation marks, is called reported speech.
- Reporting Verb: The verb of the reporting speech is called the reporting verb.
- Reported Verb: The verb of the reported speech is called the reported verb.
Changes in Person of Pronouns:
- 1st Person pronouns in reported speech are always changed according to the subject of the reporting speech.
- 2nd Person pronouns in reported speech are always changed according to the object of the reporting speech.
- 3rd Person pronouns in reported speech are not changed.
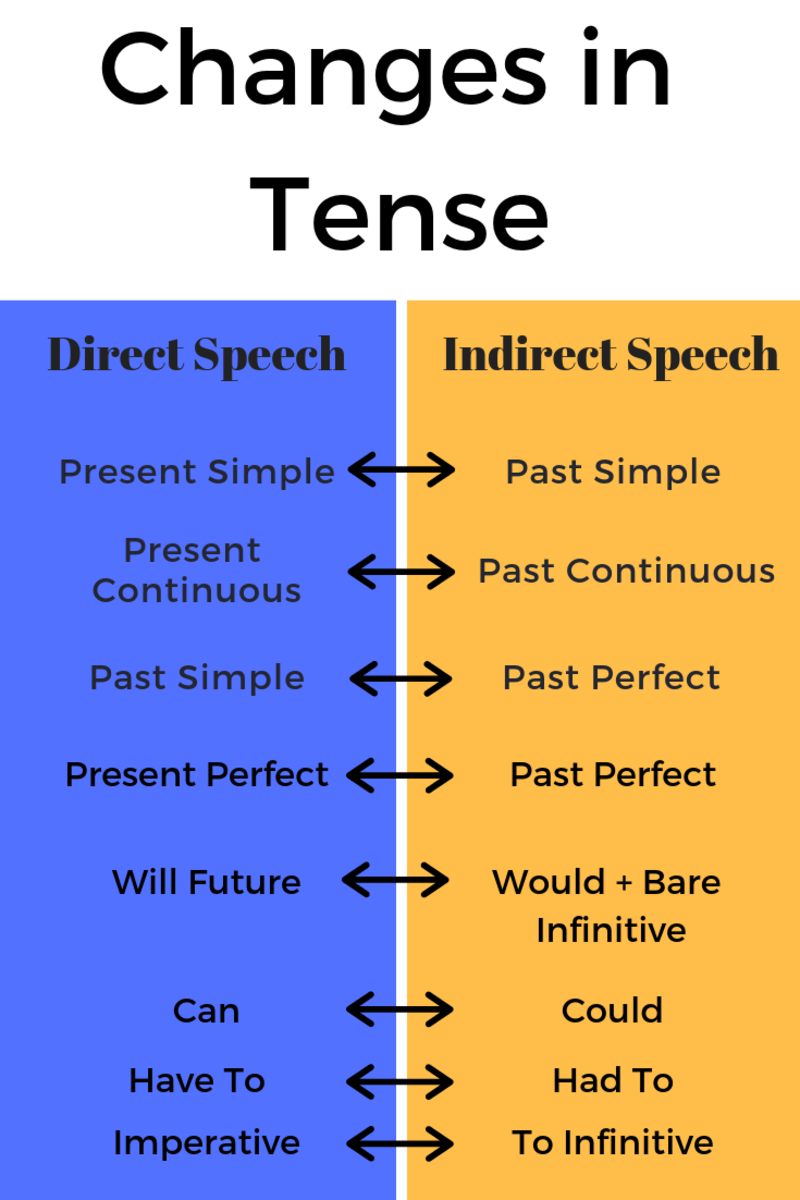
Changes in Verbs:
- If the reporting speech is in present tense or future tense, then no change is required to be made in the verb of reported speech. This verb could be in any tense i.e., present, past, or future. For example:
Direct Speech: He says, “I am ill.”Indirect Speech: He says that he is ill.Direct Speech: She says, “She sang a song.”Indirect Speech: She says that she sang a song.Direct Speech: You say, “I shall visit London.”Indirect Speech: You say that you will visit London.
- If the reporting verb is in past tense, then reported verb will be changed as per the following criterion:
- Present indefinite tense is changed into past indefinite tense. For example:
Direct Speech: They said, “They take exercise every day.”
Indirect Speech: They said that they took exercise every day.
- Present continuous is changed into past continuous tense.
Direct Speech: They said, “They are taking exercise every day.”
Indirect Speech: They said that they were taking exercise every day.
- Present perfect is changed into the past perfect tense.
Direct Speech: They said, “They have taken exercise.”
Indirect Speech: They said that they had taken exercise.
- Present perfect continuous tense is changed into past perfect continuous tense.
Direct Speech: They said, “They have been taking exercise since morning.”
Indirect Speech: They said that they had been taking exercise since morning.
- Past indefinite is changed into past perfect tense.
Direct Speech: They said, “They took exercise.”
Indirect Speech: They said that they had taken exercise.
- Past continuous tense is changed into past perfect continuous tense.
Direct Speech: They said, “They were taking exercise.”
Indirect Speech: They said that they had been taking exercise.
- No changes are required to be made into past perfect and past perfect continuous tenses.
Direct Speech: They said, “They had taken exercise.”
Indirect Speech: They said that they had taken exercise.
- In Future Tense, while no changes are made except shall and will are changed into would.
Direct Speech: They said, “They will take exercise.”
Indirect Speech: They said that they would take exercise.
Important Word Changes
Words
|
Changed Into
|
Direct Speech
|
Indirect Speech
|
|---|---|---|---|
| This | That | He says, “He wants to buy this book.” | He says that he wants to buy that book. |
| These | Those | He says, “He wants to buy these books.” | He says that he wants to buy those books. |
| Here | There | She says, “Everybody was here.” | She says that everybody was there. |
| Now | Then | They say, “It’s ten o’clock now.” | They say that it’s ten o’clock then. |
| Sir | Respectfully | They said, “Sir, the time is over.” | They said respectfully that the time was over. |
| Madam | Respecfully | They said, "Madam, the time is over." | They said respectfully that the time was over. |
| Today | That Day | She said, “I am going to London today.” | She said that she was going to London that day. |
| Yesterday | The Previous Day | She said, “I visited Oxford University yesterday.” | She said that she had visited Oxford University the previous day. |
| Tomorrow | Following Day or Next Day | She said, “I am going to London tomorrow.” | She said that she was going to London the next day. |
| Tonigh | That Night | She said, “I am going to see him tonight.” | She said that she was going to see him that night. |
| Good Morning, Good Evening, Good Day | Greeted | She said, “Good morning, Sir David.” | She greeted Sir David. |
The rules above are mandatory for converting direct speech into indirect speech. Hence, they should be memorized thoroughly. The following examples cover all the aforementioned rules. So, focus on every sentence to know how the above-mentioned rules have been used here.
Examples of Direct And Indirect Speech
Direct Speech
|
Indirect Speech
|
|---|---|
| She says, “I eat an apple a day.” | She says that she eats an apple a day. |
| He will say, “My brother will help her.” | He will say that his brother will help her. |
| We said, “We go for a walk every day.” | We said that we went for a walk every day. |
| You say, “I went to London yesterday.” | You say that you went to London the previous day. |
| He said, “My father is playing cricket with me.” | He said that his father was playing cricket with him. |
| They said, “We have completed our homework.” | They said that they had completed their homework. |
| She said, “I have been waiting for him since last morning.” | She said that she had been waiting for him since last morning. |
| She said, “I bought a book.” | She said that she had bought a book. |
| They said, “We were celebrating Eid yesterday.” | They said that they had been celebrating Eid the previous day. |
| We said, “We had been waiting since morning.” | We said that we had been waiting since morning. |
| He said to me, “I will not give you any medicine without prescription.” | He said to me that he would not give me any medicine without a prescription. |
| Rafiq said, “I shall leave for London tomorrow.” | Rafiq said that he would leave for London the next day. |
| She said, “I shall be visiting my college tomorrow.” | She said that she would be visiting her college the following day. |
| They said, “It will have been snowing since morning.” | They said that it would have been snowing since morning. |
THANK YOU
HOPING YOUR DREAM COME TRUE ☺️
Komentar
Posting Komentar